Sumer (pronounced "Shoomer"), Biblical Shi-nar, is the oldest known civilization in the world. The people who arrived in the plain between the Tigris and Euphrates over 5,000 years ago handed down to us the art of writing, the wheel, and the foundation of many of our myths and legends.
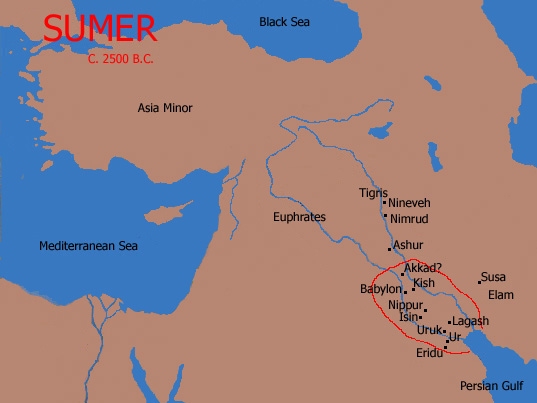
Sumerian City-States
Sumerian city-states were the center of the Sumerian culture. The cities probably began as centers of religious worship and festivities. As the cities grew people began to take refuge behind their walls from the growing number of raiders who preyed upon the open defenseless villages. City-states were independent entities who shared a common culture, though they were sometimes united under a single king.
Abu Salabikh
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
Adab
- Patron Deity: Ninhursag
- Modern Day Name: Tell Bismya.
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible.
Agade
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
Akshak
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
Anshan
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: Tepe Maylan
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
- Notes: major city of Elam
Apisala
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Aratta
- Patron Deity: Inanna
- Modern Day Name:
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: According to legend, Aratta was the first city built by the gods. It was created to house the gods newly created servants, mortal men. The exact location of Aratta is not known, though it is believed to be located in the Zagros mountains.
Babil
- Patron Deity: Marduk
- Modern Day Name:
- Biblical Name: Babylon, Babel of Genesis
Bad-tibira
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: Tell ad-Medain/Medina
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: Bad-tibira is one of the five antediluvian cities mentioned in the king list.
Dabrum
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: Tell Jidr
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Der
- Patron Deity: Ishtar
- Modern Day Name: Tell Agar/Badrah
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Dilbat
- Patron Deity: Urash
- Modern Day Name: Tell Deylum
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Enegi
- Patron Deity: Ninazu
- Modern Day Name: Umm al-Wawiya
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Eridu
- Patron Deity: Enki
- Modern Day Name: Abu Shahrein
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: Eridu is one of the five antediluvian cities mentioned in the king list. It is the oldest known Sumerian city and served as the first capital of the kingdom.
Eshnunna
- Patron Deity: Ninazu
- Modern Day Name: Tell Asmar
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Girsu
- Patron Deity: Ningirsu
- Modern Day Name: Tello
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Hit
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
Isin
- Patron Deity: Gula
- Modern Day Name: al-Bahriyat
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Jemdet Nasr
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
Kesh
- Patron Deity: Ninhursag
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
- Notes: The location of Kesh is not certain, though it was probably south of Adab.
Ki-An
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Kish
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: Al Ukhaimir
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: According to the Sumerian King List, Kish was the first post-diluvian capital of Sumer.
Kisurra
- Patron Deity: Ninurta
- Modern Day Name: Abu-Hatab
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Kuara/Kisiga
- Patron Deity: Meslamtea
- Modern Day Name:
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Kutallu
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: Tell Sift
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Kutha/Kutu
- Patron Deity: Nergal
- Modern Day Name:
- Biblical Name: mentioned as Cuthah in II Kings 17.24 and Cuth in II Kings 17.30
Lagash
- Patron Deity: Ningirsu
- Modern Day Name: Al-Hiba
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
- Notes: Flourishing by 2400, though inhabitation goes back to at least the 4th millenium
Larak
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: Larak is one of the five antediluvian cities mentioned in the king list. The location of Larak has never been located.
Larsa
- Patron Deity: Shamash
- Modern Day Name: Senkere/Sankarah
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
- Notes: Probably founded in prehistoric times.
Marad
- Patron Deity: Ninurta
- Modern Day Name: Wannat es-Sadum
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Nagsu
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Nina/Sirara
- Patron Deity: Nanshe
- Modern Day Name: Zurghul
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Nippur
- Patron Deity: Enlil
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: Nippur was not a political city serving more of a religious center. Kings ascending the throne in another cities, such as Ur and Kish, sought recognition from Ekur, the temple of Enlil, which was located in Nippur.
Shuruppak
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: Shuruppak is one of the five antediluvian cities mentioned in the king list.
Sippar
- Patron Deity: Shamash
- Modern Day Name:
- Biblical Name: --
- Notes: Sippar is one of the five antediluvian cities mentioned in the king list.
Susa
- Patron Deity: Inshushinak
- Modern Day Name: Shush
- Biblical Name: Shushan
- Notes: Susa was the capital of Elam.
Ubaid
- Patron Deity: --
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: --
Umma
- Patron Deity: Shara
- Modern Day Name: Tell Jokha
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Ur
- Patron Deity: Nanna
- Modern Day Name: --
- Biblical Name: Ur
- Notes: Ur is one of the more well-known of the ancient Sumerian cities. According to the Bible Ur was the home of Abraham. Ur was one of the first settlements founded by the Ubaids c. 4000 B.C. It eventually became of the most prosperous city-states of Sumer.
Uruk
- Patron Deity: Inanna
- Modern Day Name:
- Biblical Name: Erech
- Notes: Uruk is more well-known from its Biblical name of Erech. It was the largest city of ancient Sumer. It was an important religious center. According to legend Uruk was also the home of Gilgamesh, the famous Sumerian king, hero, and god.
Zabalam
- Patron Deity: Inanna
- Modern Day Name: Ibzeikh
- Biblical Name: not mentioned in the Bible
Cuneiform
Cuneiform, from the Latin word cuneus (wedge), is the term used to describe the earliest known writing. The advent of writing and its subsequent evolution is not clearly known. It is not known if the invention of writing was the act of a single genius, an effort by a group of people, or was the result of a slow process. A popular theory involves the use of three-dimensional clay tokens. These clay tokens were pressed into wet clay. Eventually scribes began to draw two-dimensional shapes into the clay to represent the tokens.
Whatever the evolution, by 4000 B.C. the Sumerians developed a form of pictograph writing. Early pictograph writing had several disadvantages. Early pictographs could not express abstract ideas, only physical objects. Some of the symbols were too complicated to draw with the writing instruments the scribes had available to them. Lastly, there were no standards leading to great variation between the many pictographs in use. This would lead into the next evolution of writing.
To overcome the limitations imposed by a pure pictograph script scribes began to develop phonetics. For example, the words for "bee" and "leaf" could be combined to form "belief." Over time the pictographs became stylized and shortened into wedge-shaped imprints allowing syllables to be formed instead of pictures and allowed the script to become standardized. By 3000 B.C. cuneiform was developed.
Cuneiform was initially utilized for accounting purposes. Transactions were recorded on clay tablets and were sometimes sealed in clay envelopes to protect against fraud and tampering. The Sumerian cuneiform script became the standard script for Mesopotamia as it was adopted by the Akkadians, Assyrians, Babylonians, and spread as far as Persia and Egypt. Cuneiform proved to be a very resilient script. It would undergo several transformations over the ensuing centuries and it could still be found in use in astronomical charts as late as 75 A.D.
Sumerian Legacy
- wheel
- mathematical symbols
- writing
- irrigation
- cities

