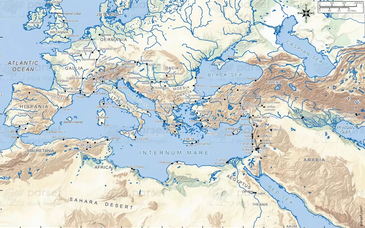
The Ancient Near East is a region that is often referred to as the cradle of civilization. It is a vast area that includes modern-day Iraq, Iran, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Turkey, and parts of Egypt and Greece. The region is home to some of the earliest known human settlements, and it was the birthplace of many important cultural and technological innovations, such as writing, agriculture, and the wheel.
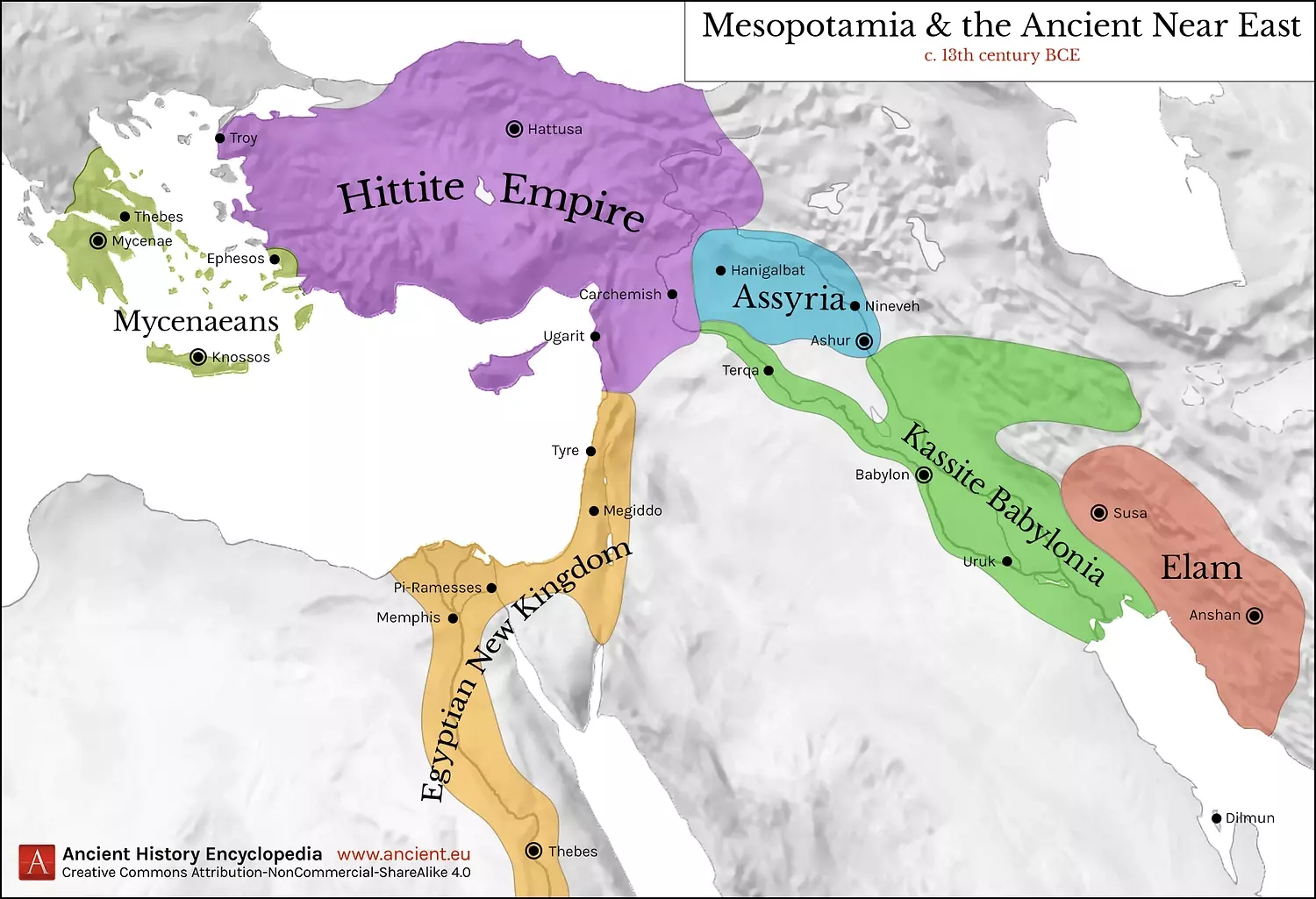
The Ancient Near East was a region of great diversity. It was home to many different cultures, languages, and religions. Some of the most important civilizations of the Ancient Near East include:
- Mesopotamia: This region was home to the Sumerians,
Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians.
The Sumerians were the first people to develop writing, and they also made important contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and engineering.
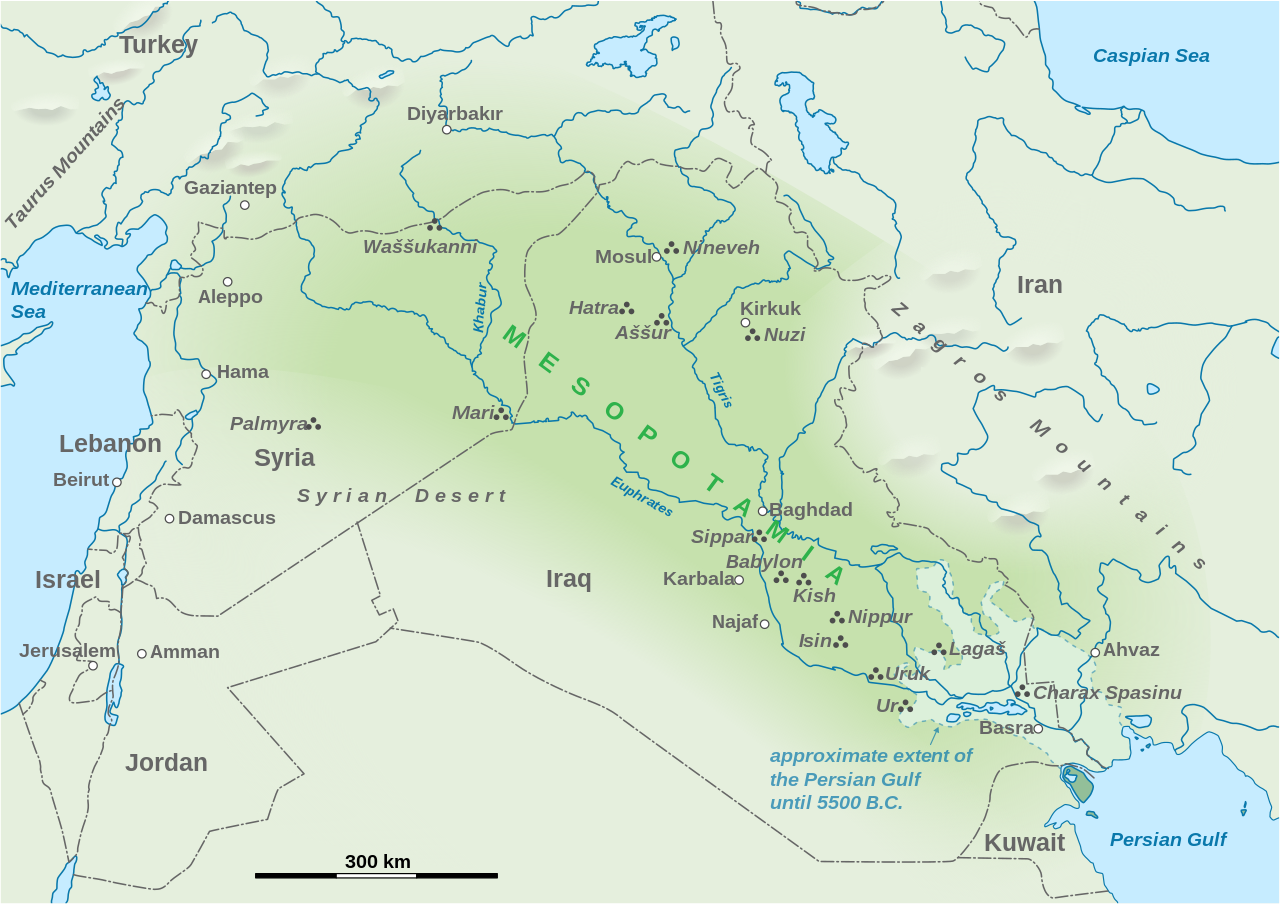
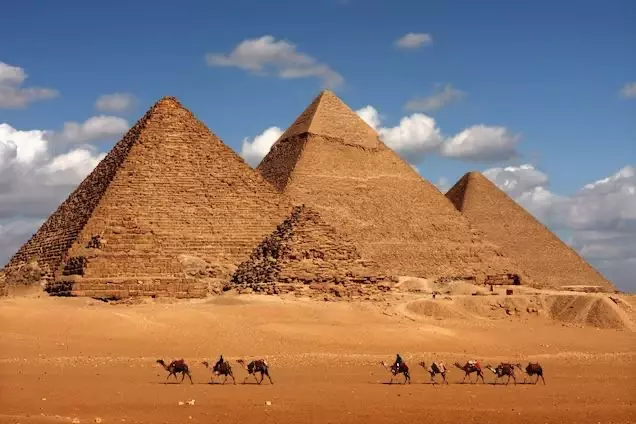
Mesopotamia - Egypt: This ancient civilization was located in the Nile Valley.
The Egyptians were known for their pyramids, hieroglyphs,
and papyrus scrolls.

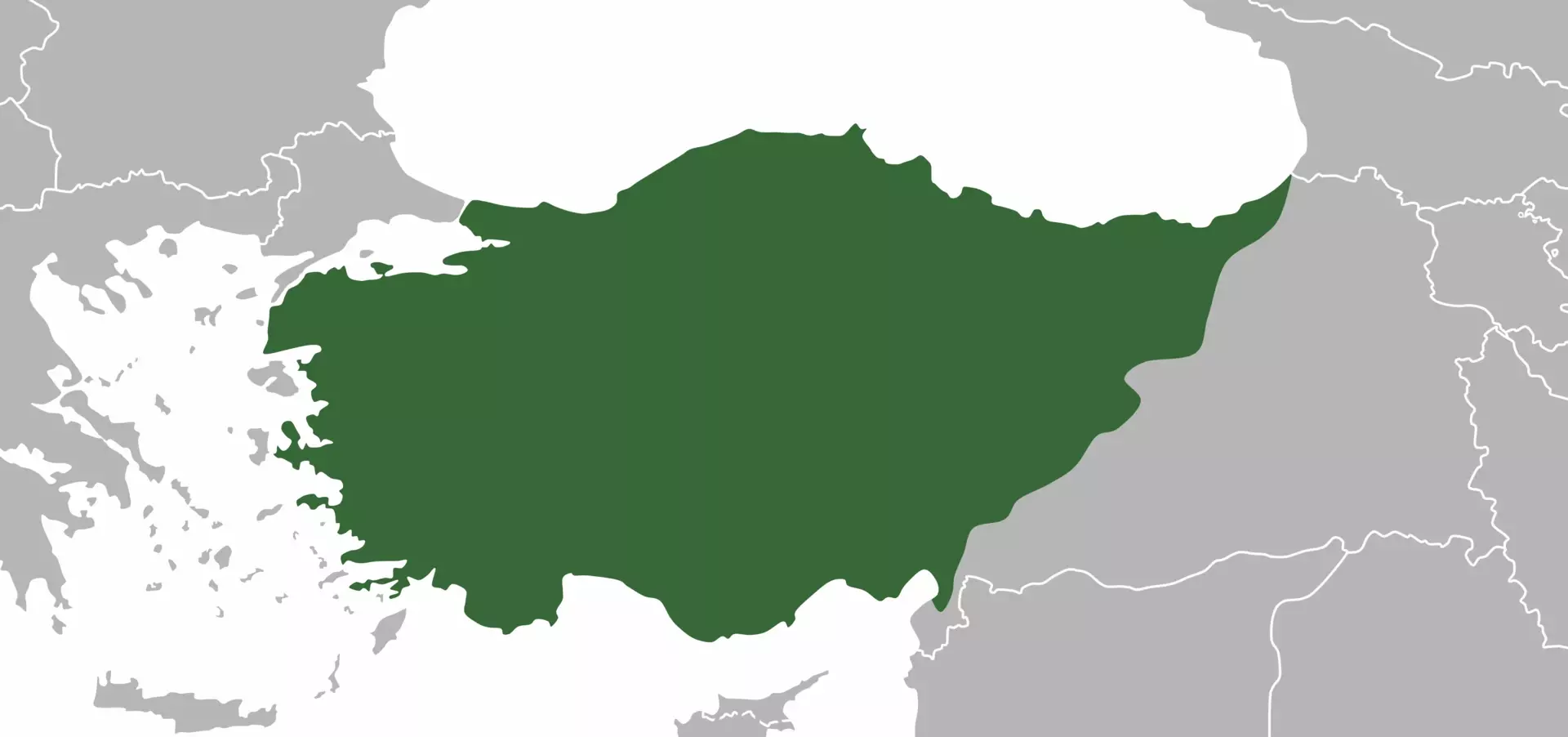
Egypt - Anatolia: This region is located in modern-day Turkey. The Hittites were the
most powerful civilization in Anatolia, and they were known for their military prowess and their advanced legal system.
Anatolia - The Levant: This region is located in modern-day Syria,
Lebanon, Israel, and Jordan. The Phoenicians were the most important civilization in the Levant, and they were known for their maritime trade and their development
of the alphabet.
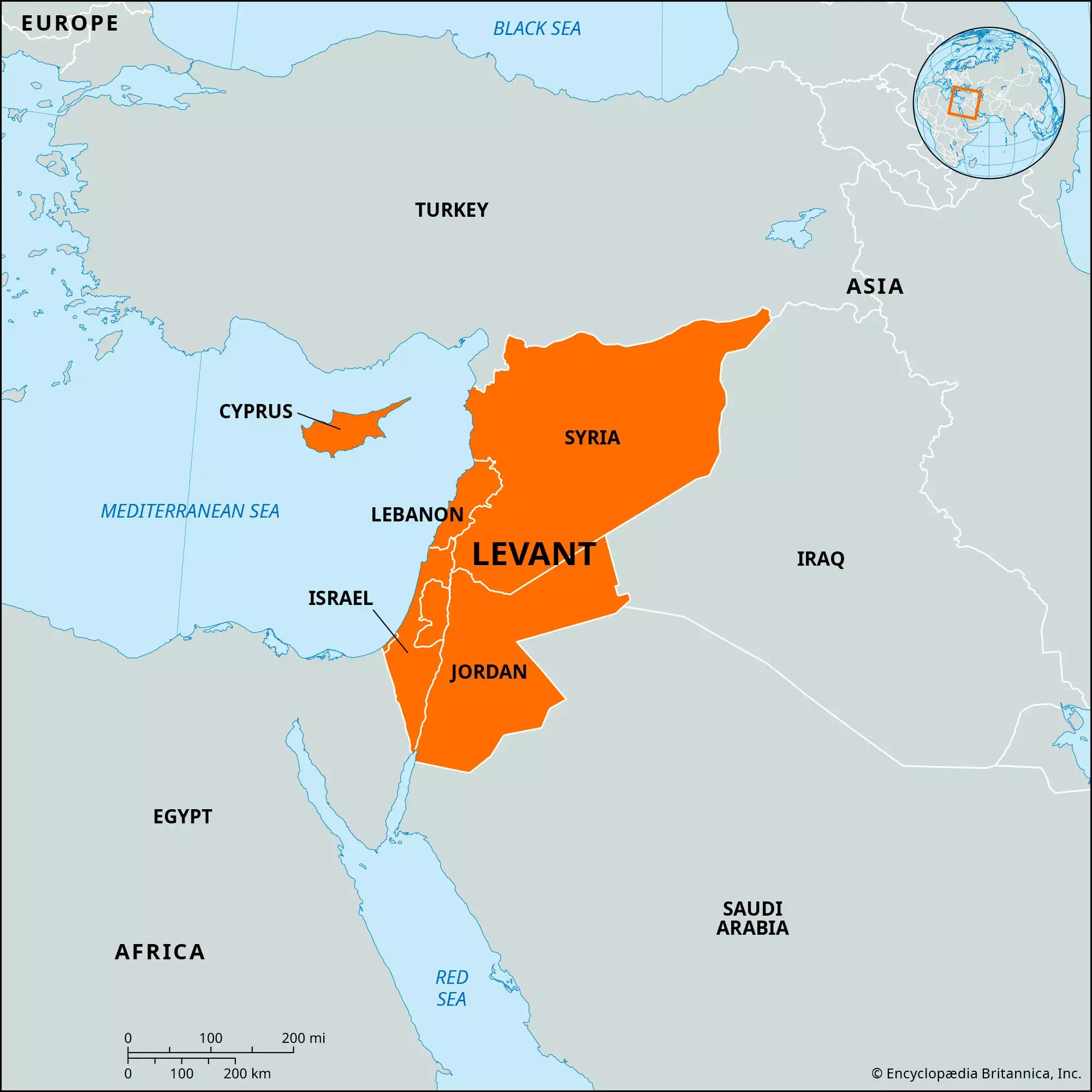
Levant
The Ancient Near East was a dynamic and constantly changing region. It was a crossroads of cultures, and it was home to many important innovations. The region's legacy can still be seen in the modern world, and it continues to be a source of fascination for scholars and archaeologists.
Here are some of the most important contributions of the Ancient Near East to the world:
- Writing: The Sumerians developed the first writing system, known as cuneiform. This system was used by many other cultures in the region, including the Akkadians,
Babylonians, and Assyrians.
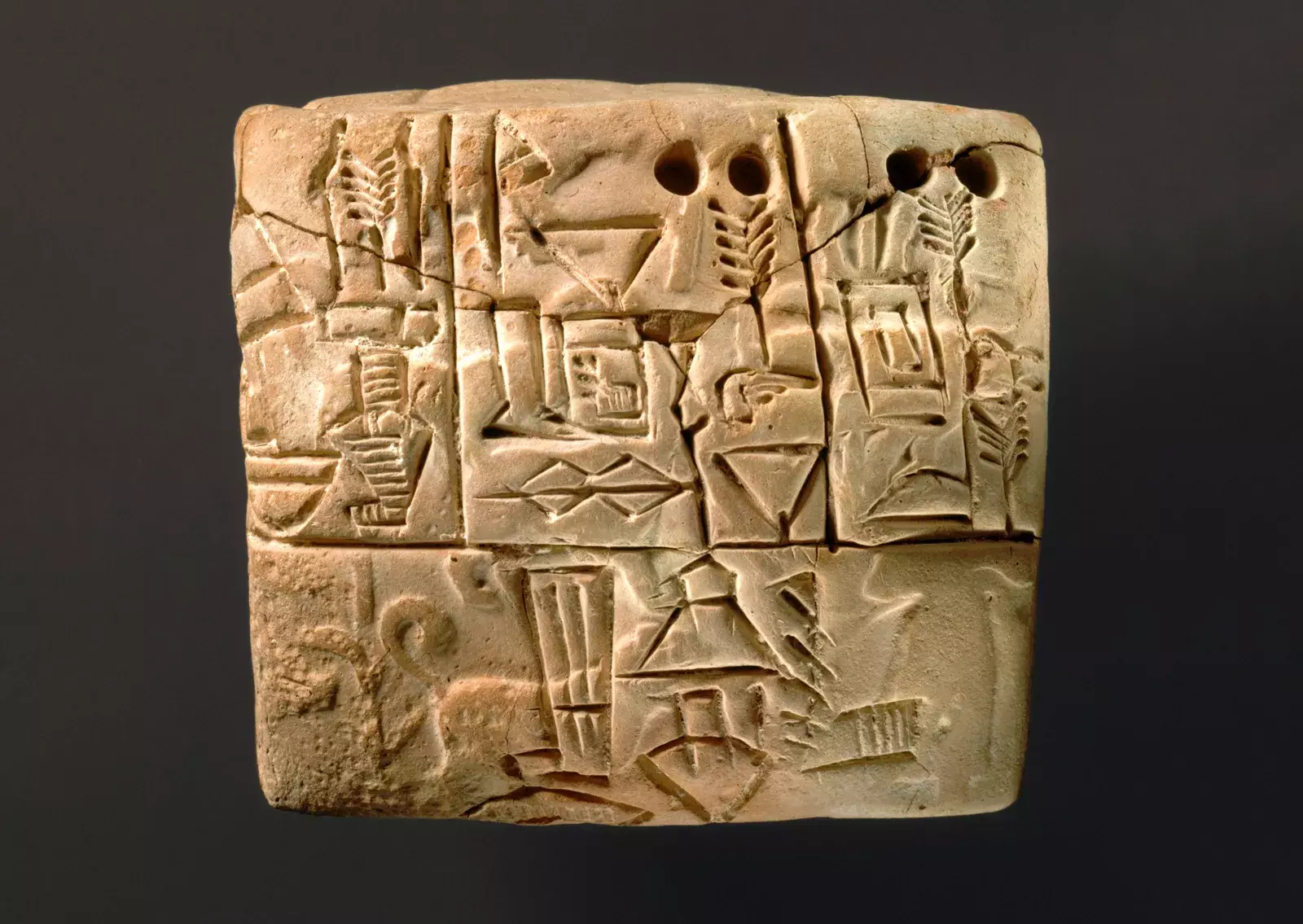

Cuneiform - Agriculture: The Ancient Near East was the birthplace of agriculture. The Sumerians, Babylonians, and Egyptians all developed sophisticated irrigation systems that allowed them to grow crops in dry areas.
- Mathematics: The Sumerians and Babylonians developed advanced mathematics, including the concept of zero.
- Astronomy: The Babylonians were the first people to develop a accurate calendar. They also made important observations of the stars and planets.
- Engineering: The Egyptians and Mesopotamians built some of the most impressive engineering feats in the ancient world, including the pyramids and the Hanging Gardens of Babylon.
- Religion: The Ancient Near East was home to many different religions, including polytheism, monotheism, and ancestor worship. These religions had a profound impact on the development of later religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
The Ancient Near East was a fascinating and complex region that played a major role in the development of human civilization. Its legacy can still be seen in the modern world, and it continues to be a source of fascination for scholars and archaeologists.