After 1380 B.C.
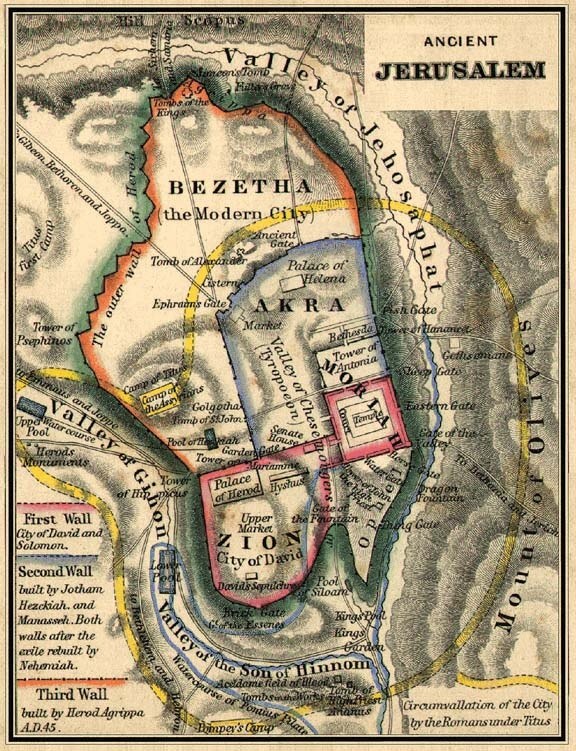
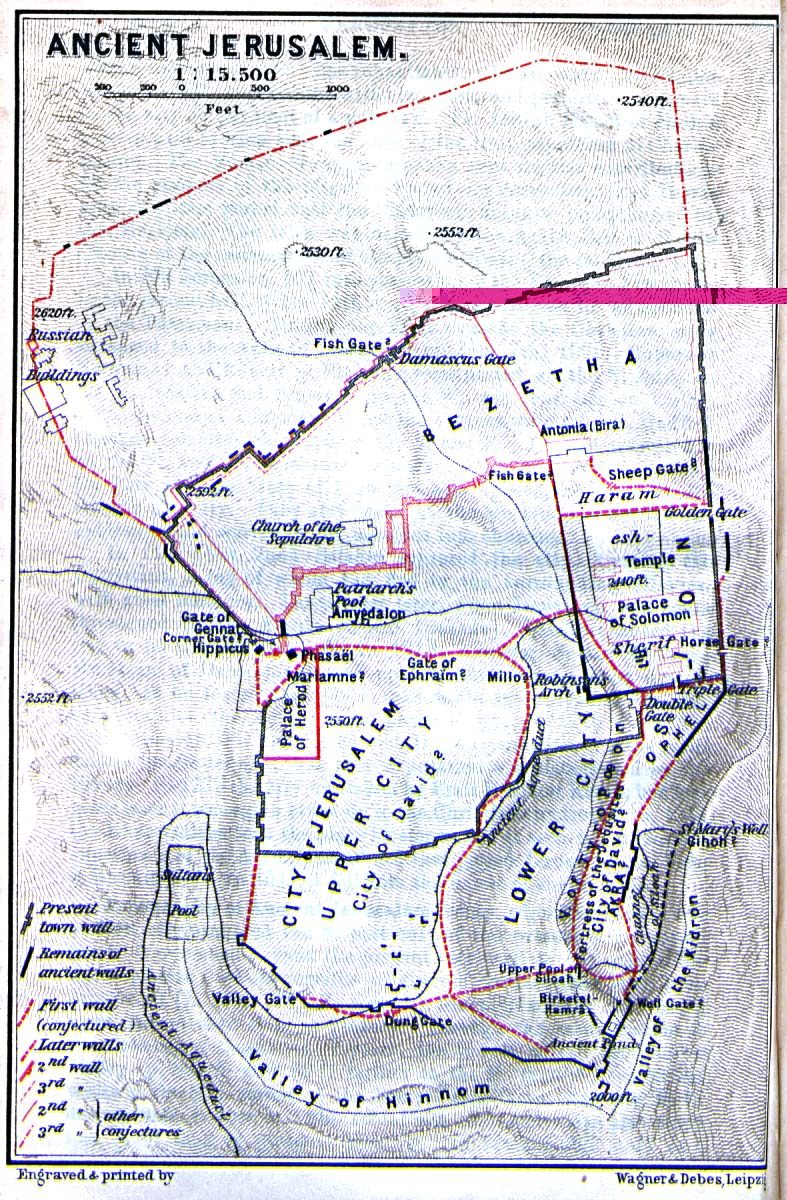
Jebus, the original name of ancient Jerusalem, is populated by the Jebusites (a Canaanite tribe). It is a city built on seven hills. A partial siege carried out by the tribe of Judah against the city (Judges 1:8) takes place a short time after the death of Joshua.
1010
David begins his rule as king after the death of Saul. His reign, however, begins with him ruling over only one Israelite tribe (his own tribe of Judah). He will not make Jerusalem his capital until he is made ruler over all Israel.
1003
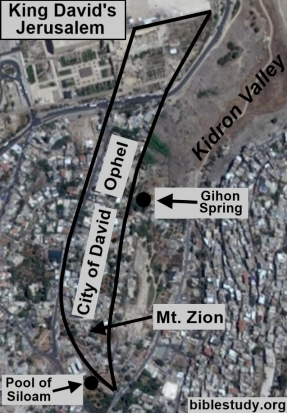
David, after ruling over only the tribe of Judah for seven and one-half years, is accepted as king over all of Israel. His first act after becoming the ruler over a united kingdom is to battle the Jebusites over control of Jerusalem. He conquers the ancient city and makes it his capital. From this time forward it is commonly referred to as "the city of David."
970
Solomon, after the death of his father David, begins his reign in Jerusalem as king of Israel.
959 - 958
King Solomon completes the building of the temple in Jerusalem dedicated to the great God.
930
Israel splits into two separate entities, with two separate ruling dynastys, after the death of Solomon. The northern ten tribes of Israel, commonly referred to as simply "Israel" in the Bible, is ruled over by Jeroboam. This kingdom will, eventually, make Samaria its capital city. The southern part of Israel, composed of the tribes of Judah, Benjamin and Levi, becomes the Kingdom of Judah. Rehoboam, the son of Solomon, rules over the kingdom from Jerusalem. He will reign for seventeen years.
925
The city is attacked by Shishak, the king of Egypt (2Chronicles 12:9, 1Kings 14:25 - 26). He is the first Egyptian Pharaoh to capture and pillage the city.
850
The city is attacked by the Philistines, Arabians and Ethiopians (2Chronicles 21:16). The royal palace is looted.
792
King Jehoash of Israel sacks Jerusalem, destroys its walls and takes King Amaziah of Judah prisoner.
735 - 732
Rezin, king of Syria, and Pekah, king of Israel, attack the city (2Chronicles 28). King Ahaz seeks the aid of Tiglath-Pileser, king of Assyria, to deliver him from these two kings.
701
Sennacherib, king of Assyria, attacks King Hezekiah (2Chronicles 32). He not only mocks the faith of those in Jerusalem who trust the Eternal will save them, he blasphemes the Lord himself. God, however, hears the vain threats of the king and has the Angel of the Lord kill 185,000 of his troops as they prepare to enter the city (2Kings 18 - 19).
597
The city falls to King Nebuchadnezzar. He takes Judah's king as prisoner to Babylon and sets up a puppet king. In 586 he will come back and destroy the city as well as burn the temple.
516
The rebuilding of the temple is completed during the reign of Persian King Darius I.
500s - 400s
Ezra, temple priests and Levites known as "The Great Assembly" complete the canonization of the Old Testament part of the Bible.
332
The city, instead of fighting a bloody battle, surrenders to Alexander the Great.
175
Antiochus IV Epiphanes becomes King of the Seleucid Empire. He begins to force Greek culture into Judea and outlaws the Sabbath and circumcision. Antiochus also sacks Jerusalem and erects an altar to Zeus in the Second Temple.
167
The Maccabean revolt against the Seleucids is started by a Jewish priest named Mattathias.
164
The Maccabees, led by Mattathias' son Judas Maccabeus, captures Jerusalem and dedicates the temple.
63
The Roman Republic, led by Pompey, occupies Palestine.
47
Julius Caesar appoints Antipater I to be procurator of Judea. Antipater is founder of the Herodian ruling dynasty that will last until 92 A.D.
40 - 37
Herod the Great is appointed King of Judea ("King of the Jews") by the Roman Senate. He is given an army and eventually conquers Judea and the city of Jerusalem.