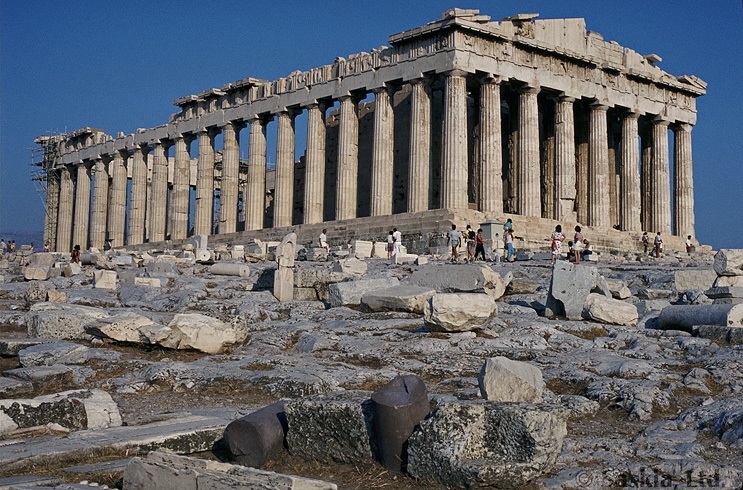
Historical Setting
When work began on the Parthenon in 447 BC, the Athenian Empire was at the height of its power. Work on the temple continued until 432; the Parthenon, then, represents the tangible and visible efflorescence of Athenian imperial power, unencumbered by the depradations of the Peloponnesian War. Likewise, it symbolizes the power and influence of the Athenian politician, Perikles, who championed its construction.
Some historians believe that Athens concluded a peace treaty with Persia in 449, two years before work began on the Parthenon. The significance of this would be that the Delian League/Athenian Empire continued to exist, even after the reason for its existence (a mutual defense league against the Persians) had ceased to be valid. In other words it was now openly acknowledged that Athens was not just the head of the Greek defense league but actually an imperial master over other Greek states. The decision by the Athenians in 454 BC to move the League treasury from the Panhellenic sanctuary at Delos to the Athenian acropolis points in the same direction. Because the Parthenon was built with League funds, the building may be read as an expression of the confidence of the Athenians in this newly naked imperialism. But the piety of this undertaking should not be underestimated; the Persians had sacked the temples on the Athenian acropolis in 480, and rebuilding them fulfilled, in Bury's words, the Athenians' "debt of gratitude to heaven for the defeat of the Mede."
Architectural Features
The Parthenon is a Doric peripteral temple, which means that it consists of a rectangular floor plan with a series of low steps on every side, and a colonnade (8 x 17) of Doric columns extending around the periphery of the entire structure. Each entrance has an additional six columns in front of it. The larger of the two interior rooms, the naos, housed the cult statue. The smaller room (the opisthodomos) was used as a treasury. Here is a plan of the temple:
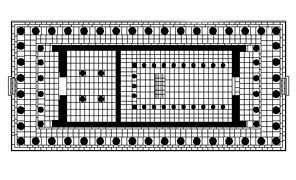
It was built to replace two earlier temples of Athena on the Acropolis. One of these, of which almost no trace remains today, stood south of the Parthenon (between the Parthenon and the Erechtheum). The other, which was still being built at the time of the Persian sack in 480, was on the same spot as the Parthenon. We know the names of the architects (Iktinos and Kallikrates) and also of the sculptor (Pheidias) who made the massive chryselephantine cult statue of the goddess.
The Orders
The three main types of columns used in Greek temples and other public buildings are Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. The truest and most basic difference among the orders has to do with proportions (Doric columns, for example, being thicker and shorter, Ionic columns taller and slimmer). As a shortcut, the orders may be distinguished most easily by their capitals (the tops of the columns). As you can see from the following examples, the Doric capital has the simplest design; the Ionic has the curlicues called volutes, and the Corinthian has the acanthus leaves:
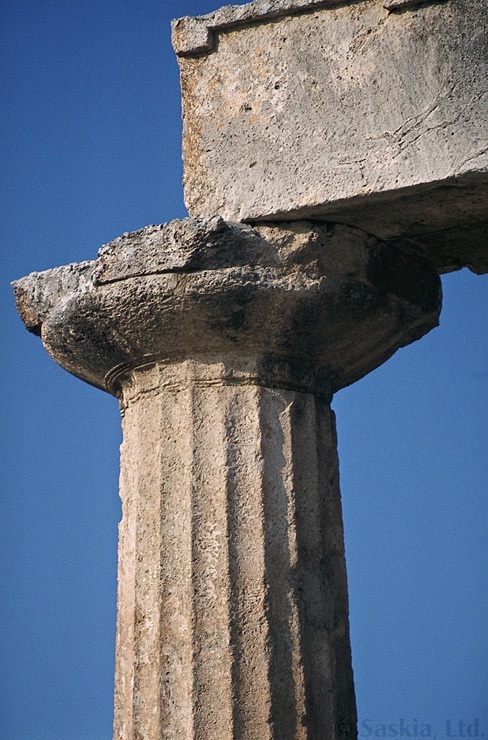



Doric is not only a type of column, but an "order"; this means that temples of the Doric order not only have this type of column, but also have a certain structure at the upper levels. The different types of orders (column plus entablature) are illustrated by these diagrams, from Perseus: Doric order, and Ionic order. The Doric order is characterized by the series of triglyphs and metopes on the entablature. Each metope was occupied by a panel of relief sculpture.
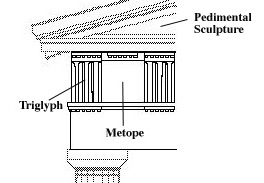
The Parthenon combines elements of the Doric and Ionic orders. Basically a Doric peripteral temple, it features a continuous sculpted frieze borrowed from the Ionic order, as well as four Ionic columns supporting the roof of the opisthodomos.
The Metopes
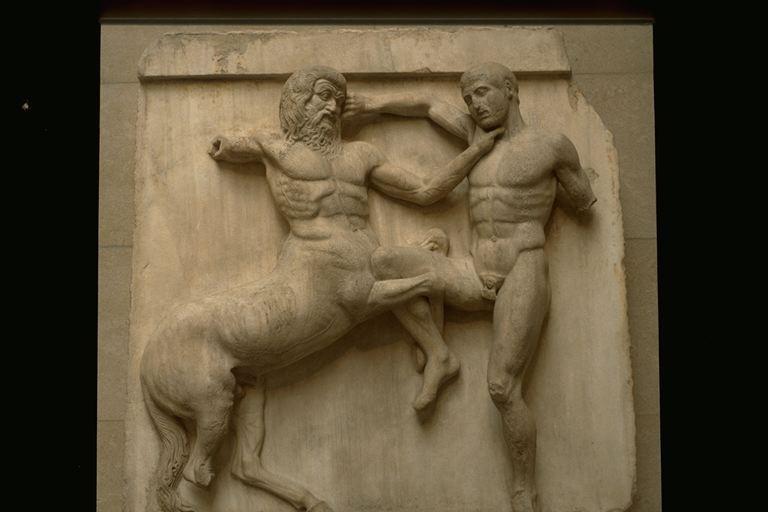
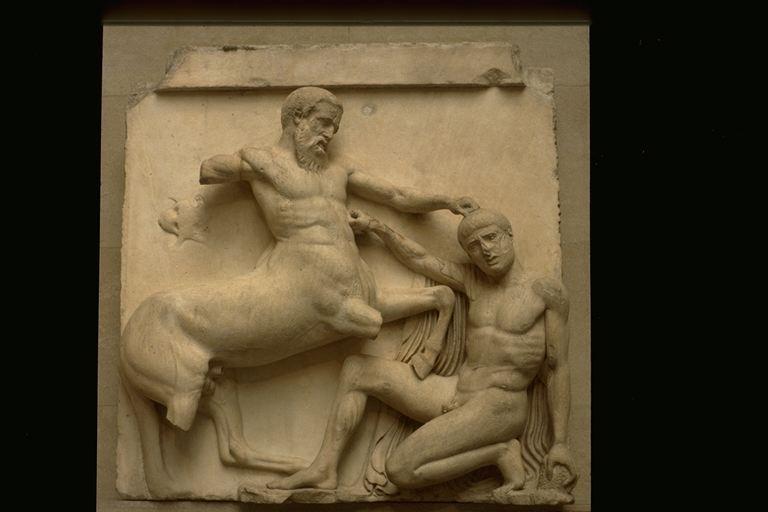
The metopes of the Parthenon all represented various instances of the struggle between the forces of order and justice, on the one hand, and criminal chaos on the other. On the west side, the mythical battle against the Amazons (Amazonomachy); on the south, the battle between the Lapiths and the Centaurs (Centauromachy); on the east, the battle between the gods and the giants (Gigantomachy); on the north, the Greeks versus the Trojans. Of the panels the best preserved are those showing the Centauromachy. Here are South Metope 31 and 30 (compare the discussion in Pollitt, Art & Experience, 82-83):


The Pedimental Sculptures
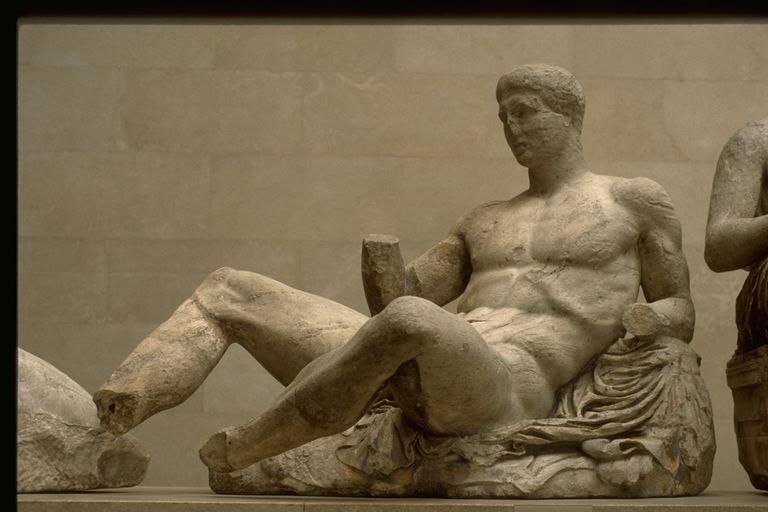
These relief sculptures, larger than those of the metopes, occupied the triangular space above the triglyphs and metopes. Those at the west end of the temple depicted the contest between Poseidon and Athena for the right to be the patron deity of Athens (Athena's gift of the olive tree was preferred over Poseidon's spring). The eastern pedimental group showed the birth of Athena from Zeus' head. The pedimental sculpture suffered badly when the Parthenon was hit by a Venetian shell in 1687 and the powder magazine inside exploded. This reclining god (probably Dionysus) from the east pediment gives some sense of the quality of the sculpture:

The Frieze
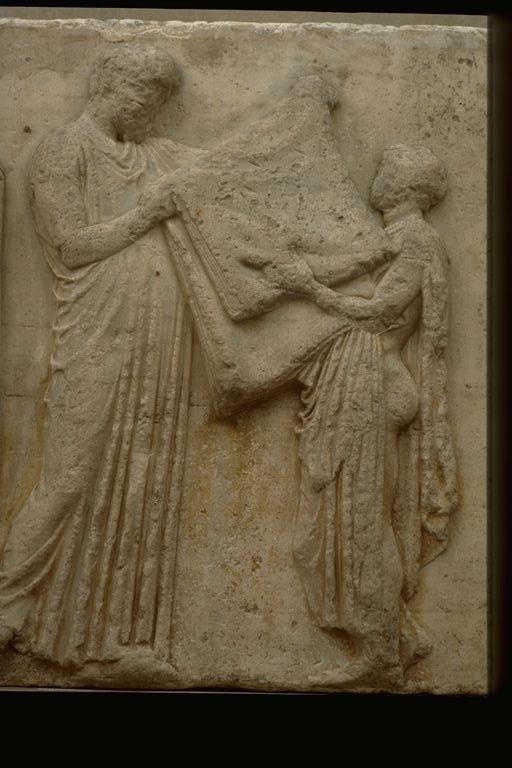
The Parthenon frieze runs around the upper edge of the temple wall. Its relatively small size (3 feet 5 inches tall) and placement (inside from the triglyphs and metopes) made it fairly hard to see from the ground. Unlike the metopes, the frieze has a single subject on all four sides. On three sides (north, west, and south) it depicts a procession of horsemen, musicians, sacrificial animals, and other figures with various ritual functions. On the east side there is a scene centered on a child handing a folded cloth to an older man. On one side of them seated gods and goddess are in attendance; on the other, two girls are carrying something. Although the state of preservation is poor, the interpretation of the subject has hotly debated. Most scholars agree that it represents the Panathenaic procession, but some think it is a mythical, "original" procession, while others believe that it is the procession which took place in the same period as the temple was built, and that this illustrates the (over-)confident spirit of the Athenians, who dared to put themselves where ordinarily only gods and heroes might be found.
